Behaviour Change
Systematic behaviour change
The behaviour change pillar in the hands4health project will systematically develop and test behaviour change campaigns targeting hand hygiene behaviour in health care facilities and schools based on the RANAS approach. The RANAS contribution to the hands4health project consists of two components: (i) Training of RanasEXPERTS and (ii) Development of RANAS behaviour change toolkits (Ranas4SCHOOLS and Ranas4HCF).
The expected result is safe and frequent hand hygiene behaviour in different user groups of health care facilities and schools. The focus will be set on health care staff and school children in particular. Local implementation partners are involved throughout the whole development and implementation process of the behaviour change campaigns. They are trained on the methodology and receive a certificate as local RanasEXPERTS.
An easy-to-use RANAS behaviour change tool-kit will be developed as part of the overall holistic approach, combining different technologies and a behaviour change component. The tool-kit will provide an off-the-shelf hand hygiene campaign for schools or health care facilities and will enable hygiene promoters to adapt the campaign based on data to their specific context.
RANAS approach of systematic behaviour change
The RANAS model is based on theories and models of health and environmental psychology and comprises the most important behavioural factors that influence the performance of human behaviours. Published in 2012 (Mosler, 2012), it has been extensively tested for various health and other behaviours and successfully applied in research and consulting projects in more than 40 countries all over the world.
The model describes the core mechanism of systematic behaviour change: there exists a set of behavioural factors – risk, attitude, norm, ability and self-regulation factors – that influence human behaviour and that can be influenced by corresponding behaviour change techniques. Contextual factors mediate and moderate these causal relations.
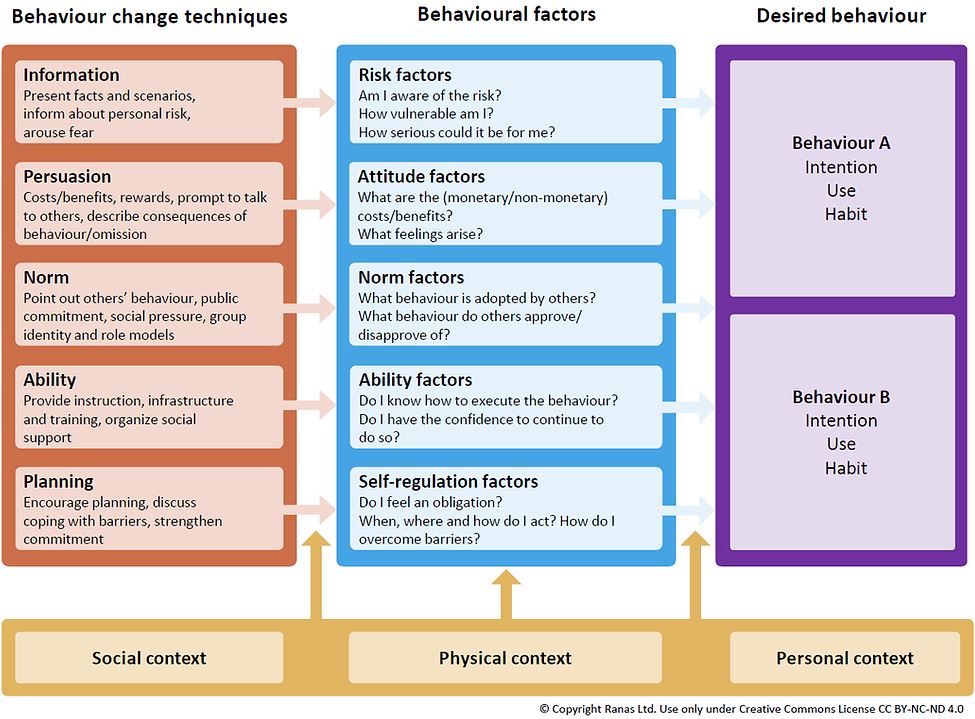
The RANAS approach determines the different steps needed to apply the model in a standardised and practical way:
- By using a short qualitative pre-survey and Focus Group Discussions, the behaviour is defined and a quantitative questionnaire is developed.
- This questionnaire is applied in a survey of several hundred individuals.
- Using the data of the survey, we conduct a doer/non-doer analysis by comparing the people who perform the behaviour frequently, consistently and thoroughly with those who do not or only irregularly perform the behaviour.
- The behavioural factors where doers and non-doers differ significantly have to be tackled by behaviour change techniques. The RANAS approach provides a catalogue of 36 behaviour change techniques that are matched to the behavioural factors.
- The selected behaviour change techniques are translated into messages and activities for a behaviour change campaign.
- The campaign is implemented and evaluated.
References & further resources
RANAS (2023). The Behaviour Change Toolkits in the hands4health project: Ranas4HCFs and Ranas4Schools.
Tamas, A. et al. (2023). Developing and testing an easy-to-use toolkit to design tailored behavior change interventions.
Mosler, H.-J. (2012). A systematic approach to behavior change interventions for the water and sanitation sector in developing countries: a conceptual model, a review, and a guideline. International Journal of Environmental Health Research, 1–19. DOI: 10.1080/09603123.2011.650156.
Other hands4health knowledge products can be found here.